Cnc machine
From
| Project: cnc machine | |
|---|---|
| 360x360px | |
| Name | cnc machine |
| Initiator | tkkrlab |
| Status | Actief |
| Skills | {{{Skillz}}} |
| Summary | bouw van cnc machine voor TkkrLab |
Contents
- 1 Zen CNC
- 1.1 Smoothieboard upgrade
- 1.2 Leveling the base
- 1.3 Some testing and milling with our new spindle
- 1.4 Who
- 1.5 Goal
- 1.6 Electronics
- 1.7 Firmware
- 1.8 Cad / Cam and other software
- 1.9 Add ons / Wishlist
- 1.10 (short) PCB milling instructions using eagle with gcode V3.6.4.2 or newer with the TkkrLab CNC (old)
- 1.11 PCB milling instructions using eagle with the TkkrLab CNC (new)
Zen CNC
After some searching, debating and comparison we have decided to spend our 500 Euro budget on the Zen toolworks 7x7 CNC.
our machine with test setup:
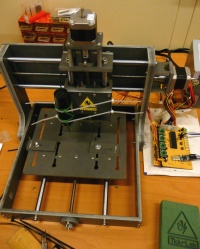
PDF Manual or wiki
First tests with pen and 1mm drill as cutting tool:
 .
. .
.
First Actual PCB drilling:

Smoothieboard upgrade
Some information on this page might be outdated now that we upgraded to a Smoothie board (MKS-SBASE, see lasercutter for more info). Limit switches have been installed as well.
Configuration of smoothieboard:
Invalid language.
You need to specify a language like this: <source lang="html4strict">...</source>
Supported languages for syntax highlighting:
4cs, 6502acme, 6502kickass, 6502tasm, 68000devpac, abap, actionscript, actionscript3, ada, algol68, apache, applescript, apt_sources, arm, asm, asp, asymptote, autoconf, autohotkey, autoit, avisynth, awk, bascomavr, bash, basic4gl, bf, bibtex, blitzbasic, bnf, boo, c, c_loadrunner, c_mac, caddcl, cadlisp, cfdg, cfm, chaiscript, cil, clojure, cmake, cobol, coffeescript, cpp, cpp-qt, csharp, css, cuesheet, d, dcl, dcpu16, dcs, delphi, diff, div, dos, dot, e, ecmascript, eiffel, email, epc, erlang, euphoria, f1, falcon, fo, fortran, freebasic, freeswitch, fsharp, gambas, gdb, genero, genie, gettext, glsl, gml, gnuplot, go, groovy, gwbasic, haskell, haxe, hicest, hq9plus, html4strict, html5, icon, idl, ini, inno, intercal, io, j, java, java5, javascript, jquery, kixtart, klonec, klonecpp, latex, lb, ldif, lisp, llvm, locobasic, logtalk, lolcode, lotusformulas, lotusscript, lscript, lsl2, lua, m68k, magiksf, make, mapbasic, matlab, mirc, mmix, modula2, modula3, mpasm, mxml, mysql, nagios, netrexx, newlisp, nsis, oberon2, objc, objeck, ocaml, ocaml-brief, octave, oobas, oorexx, oracle11, oracle8, oxygene, oz, parasail, parigp, pascal, pcre, per, perl, perl6, pf, php, php-brief, pic16, pike, pixelbender, pli, plsql, postgresql, povray, powerbuilder, powershell, proftpd, progress, prolog, properties, providex, purebasic, pycon, pys60, python, q, qbasic, rails, rebol, reg, rexx, robots, rpmspec, rsplus, ruby, sas, scala, scheme, scilab, sdlbasic, smalltalk, smarty, spark, sparql, sql, stonescript, systemverilog, tcl, teraterm, text, thinbasic, tsql, typoscript, unicon, upc, urbi, uscript, vala, vb, vbnet, vedit, verilog, vhdl, vim, visualfoxpro, visualprolog, whitespace, whois, winbatch, xbasic, xml, xorg_conf, xpp, yaml, z80, zxbasic
# NOTE Lines must not exceed 132 characters
## Robot module configurations : general handling of movement G-codes and slicing into moves
default_feed_rate 4000 # Default rate ( mm/minute ) for G1/G2/G3 moves
default_seek_rate 4000 # Default rate ( mm/minute ) for G0 moves
mm_per_arc_segment 0.0 # Fixed length for line segments that divide arcs 0 to disable
mm_max_arc_error 0.01 # The maximum error for line segments that divide arcs 0 to disable
# note it is invalid for both the above be 0
# if both are used, will use largest segment length based on radius
#mm_per_line_segment 5 # Lines can be cut into segments ( not usefull with cartesian
# coordinates robots ).
# Arm solution configuration : Cartesian robot. Translates mm positions into stepper positions
alpha_steps_per_mm 2560 # Steps per mm for alpha stepper
beta_steps_per_mm 2560 # Steps per mm for beta stepper
gamma_steps_per_mm 2560 # Steps per mm for gamma stepper
# Planner module configuration : Look-ahead and acceleration configuration
planner_queue_size 32 # DO NOT CHANGE THIS UNLESS YOU KNOW EXACTLY WHAT YOU ARE DOING
acceleration 3000 # Acceleration in mm/second/second.
#z_acceleration 500 # Acceleration for Z only moves in mm/s^2, 0 uses acceleration which is the default. DO NOT SET ON A DELTA
acceleration_ticks_per_second 1000 # Number of times per second the speed is updated
junction_deviation 0.05 # Similar to the old "max_jerk", in millimeters,
# see https://github.com/grbl/grbl/blob/master/planner.c
# and https://github.com/grbl/grbl/wiki/Configuring-Grbl-v0.8
# Lower values mean being more careful, higher values means being
# faster and have more jerk
#z_junction_deviation 0.0 # for Z only moves, -1 uses junction_deviation, zero disables junction_deviation on z moves DO NOT SET ON A DELTA
#minimum_planner_speed 0.0 # sets the minimum planner speed in mm/sec
# Stepper module configuration
microseconds_per_step_pulse 1 # Duration of step pulses to stepper drivers, in microseconds
base_stepping_frequency 100000 # Base frequency for stepping
# Cartesian axis speed limits
x_axis_max_speed 300 # mm/min
y_axis_max_speed 300 # mm/min
z_axis_max_speed 300 # mm/min
# Stepper module pins ( ports, and pin numbers, appending "!" to the number will invert a pin )
alpha_step_pin 2.0 # Pin for alpha stepper step signal
alpha_dir_pin 0.5 # Pin for alpha stepper direction
alpha_en_pin 0.4 # Pin for alpha enable pin
alpha_current 0.5 # X stepper motor current
alpha_max_rate 100000.0 # mm/min
beta_step_pin 2.1 # Pin for beta stepper step signal
beta_dir_pin 0.11! # Pin for beta stepper direction
beta_en_pin 0.10 # Pin for beta enable
beta_current 0.5 # Y stepper motor current
beta_max_rate 100000.0 # mm/min
gamma_step_pin 2.2 # Pin for gamma stepper step signal
gamma_dir_pin 0.20 # Pin for gamma stepper direction
gamma_en_pin 0.19 # Pin for gamma enable
gamma_current 0.5 # Z stepper motor current
gamma_max_rate 100000.0 # mm/min
## System configuration
# Serial communications configuration ( baud rate defaults to 9600 if undefined )
uart0.baud_rate 115200 # Baud rate for the default hardware serial port
second_usb_serial_enable false # This enables a second usb serial port (to have both pronterface
# and a terminal connected)
#leds_disable true # disable using leds after config loaded
#play_led_disable true # disable the play led
# Kill button (used to be called pause) maybe assigned to a different pin, set to the onboard pin by default
kill_button_enable true # set to true to enable a kill button
kill_button_pin 2.12 # kill button pin. default is same as pause button 2.12 (2.11 is another good choice)
#msd_disable false # disable the MSD (USB SDCARD) when set to true (needs special binary)
#dfu_enable false # for linux developers, set to true to enable DFU
#watchdog_timeout 10 # watchdog timeout in seconds, default is 10, set to 0 to disable the watchdog
# Only needed on a smoothieboard
currentcontrol_module_enable true #
## Extruder module configuration
extruder.hotend.enable false # Whether to activate the extruder module at all. All configuration is ignored if false
extruder.hotend.steps_per_mm 140 # Steps per mm for extruder stepper
extruder.hotend.default_feed_rate 600 # Default rate ( mm/minute ) for moves where only the extruder moves
extruder.hotend.acceleration 500 # Acceleration for the stepper motor mm/sec²
extruder.hotend.max_speed 50 # mm/s
extruder.hotend.step_pin 2.3 # Pin for extruder step signal
extruder.hotend.dir_pin 0.22 # Pin for extruder dir signal
extruder.hotend.en_pin 0.21 # Pin for extruder enable signal
# extruder offset
#extruder.hotend.x_offset 0 # x offset from origin in mm
#extruder.hotend.y_offset 0 # y offset from origin in mm
#extruder.hotend.z_offset 0 # z offset from origin in mm
# firmware retract settings when using G10/G11, these are the defaults if not defined, must be defined for each extruder if not using the defaults
#extruder.hotend.retract_length 3 # retract length in mm
#extruder.hotend.retract_feedrate 45 # retract feedrate in mm/sec
#extruder.hotend.retract_recover_length 0 # additional length for recover
#extruder.hotend.retract_recover_feedrate 8 # recover feedrate in mm/sec (should be less than retract feedrate)
#extruder.hotend.retract_zlift_length 0 # zlift on retract in mm, 0 disables
#extruder.hotend.retract_zlift_feedrate 6000 # zlift feedrate in mm/min (Note mm/min NOT mm/sec)
delta_current 1.5 # First extruder stepper motor current
# Second extruder module configuration
#extruder.hotend2.enable true # Whether to activate the extruder module at all. All configuration is ignored if false
#extruder.hotend2.steps_per_mm 140 # Steps per mm for extruder stepper
#extruder.hotend2.default_feed_rate 600 # Default rate ( mm/minute ) for moves where only the extruder moves
#extruder.hotend2.acceleration 500 # Acceleration for the stepper motor, as of 0.6, arbitrary ratio
#extruder.hotend2.max_speed 50 # mm/s
#extruder.hotend2.step_pin 2.8 # Pin for extruder step signal
#extruder.hotend2.dir_pin 2.13 # Pin for extruder dir signal
#extruder.hotend2.en_pin 4.29 # Pin for extruder enable signal
#extruder.hotend2.x_offset 0 # x offset from origin in mm
#extruder.hotend2.y_offset 25.0 # y offset from origin in mm
#extruder.hotend2.z_offset 0 # z offset from origin in mm
#epsilon_current 1.5 # Second extruder stepper motor current
## Laser module configuration
laser_module_enable false # Whether to activate the laser module at all. All configuration is
# ignored if false.
#laser_module_pin 2.5 # this pin will be PWMed to control the laser. Only P2.0 - P2.5, P1.18, P1.20, P1.21, P1.23, P1.24, P1.26, P3.25, P3.26
# can be used since laser requires hardware PWM
#laser_module_maximum_power 1.0 # this is the maximum duty cycle that will be applied to the laser
#laser_module_minimum_power 0.0 # This is a value just below the minimum duty cycle that keeps the laser
# active without actually burning.
#laser_module_default_power 0.8 # This is the default laser power that will be used for cuts if a power has not been specified. The value is a scale between
# the maximum and minimum power levels specified above
#laser_module_pwm_period 20 # this sets the pwm frequency as the period in microseconds
## Temperature control configuration
# First hotend configuration
temperature_control.hotend.enable false # Whether to activate this ( "hotend" ) module at all.
# All configuration is ignored if false.
temperature_control.hotend.thermistor_pin 0.23 # Pin for the thermistor to read
temperature_control.hotend.heater_pin 2.7 # Pin that controls the heater, set to nc if a readonly thermistor is being defined
temperature_control.hotend.thermistor EPCOS100K # see http://smoothieware.org/temperaturecontrol#toc5
#temperature_control.hotend.beta 4066 # or set the beta value
temperature_control.hotend.set_m_code 104 #
temperature_control.hotend.set_and_wait_m_code 109 #
temperature_control.hotend.designator T #
#temperature_control.hotend.max_temp 300 # Set maximum temperature - Will prevent heating above 300 by default
#temperature_control.hotend.min_temp 0 # Set minimum temperature - Will prevent heating below if set
#temperature_control.hotend.p_factor 13.7 # permanently set the PID values after an auto pid
#temperature_control.hotend.i_factor 0.097 #
#temperature_control.hotend.d_factor 24 #
#temperature_control.hotend.max_pwm 64 # max pwm, 64 is a good value if driving a 12v resistor with 24v.
# Second hotend configuration
#temperature_control.hotend2.enable true # Whether to activate this ( "hotend" ) module at all.
# All configuration is ignored if false.
#temperature_control.hotend2.thermistor_pin 0.25 # Pin for the thermistor to read
#temperature_control.hotend2.heater_pin 1.23 # Pin that controls the heater
#temperature_control.hotend2.thermistor EPCOS100K # see http://smoothieware.org/temperaturecontrol#toc5
##temperature_control.hotend2.beta 4066 # or set the beta value
#temperature_control.hotend2.set_m_code 104 #
#temperature_control.hotend2.set_and_wait_m_code 109 #
#temperature_control.hotend2.designator T1 #
#temperature_control.hotend2.p_factor 13.7 # permanently set the PID values after an auto pid
#temperature_control.hotend2.i_factor 0.097 #
#temperature_control.hotend2.d_factor 24 #
#temperature_control.hotend2.max_pwm 64 # max pwm, 64 is a good value if driving a 12v resistor with 24v.
temperature_control.bed.enable true #
temperature_control.bed.thermistor_pin 0.24 #
temperature_control.bed.heater_pin 2.5 #
temperature_control.bed.thermistor Honeywell100K # see http://smoothieware.org/temperaturecontrol#toc5
#temperature_control.bed.beta 3974 # or set the beta value
temperature_control.bed.set_m_code 140 #
temperature_control.bed.set_and_wait_m_code 190 #
temperature_control.bed.designator B #
#temperature_control.bed.bang_bang false # set to true to use bang bang control rather than PID
#temperature_control.bed.hysteresis 2.0 # set to the temperature in degrees C to use as hysteresis
# when using bang bang
## Switch module for fan control
switch.fan.enable false #
switch.fan.input_on_command M106 #
switch.fan.input_off_command M107 #
switch.fan.output_pin 2.6 #
switch.fan.output_type pwm # pwm output settable with S parameter in the input_on_comand
#switch.fan.max_pwm 255 # set max pwm for the pin default is 255
#switch.misc.enable true #
#switch.misc.input_on_command M42 #
#switch.misc.input_off_command M43 #
#switch.misc.output_pin 2.4 #
#switch.misc.output_type digital # just an on or off pin
# Switch module for spindle control
#switch.spindle.enable false #
## Temperatureswitch :
# automatically toggle a switch at a specified temperature. Different ones of these may be defined to monitor different temperatures and switch different swithxes
# useful to turn on a fan or water pump to cool the hotend
#temperatureswitch.hotend.enable true #
#temperatureswitch.hotend.designator T # first character of the temperature control designator to use as the temperature sensor to monitor
#temperatureswitch.hotend.switch misc # select which switch to use, matches the name of the defined switch
#temperatureswitch.hotend.threshold_temp 60.0 # temperature to turn on (if rising) or off the switch
#temperatureswitch.hotend.heatup_poll 15 # poll heatup at 15 sec intervals
#temperatureswitch.hotend.cooldown_poll 60 # poll cooldown at 60 sec intervals
## Endstops
endstops_enable true # the endstop module is enabled by default and can be disabled here
#corexy_homing false # set to true if homing on a hbot or corexy
alpha_min_endstop 1.24^ # add a ! to invert if endstop is NO connected to ground
alpha_max_endstop 1.25^ # NOTE set to nc if this is not installed
alpha_homing_direction home_to_min # or set to home_to_max and set alpha_max
alpha_min -5 # this gets loaded after homing when home_to_min is set
alpha_max 300 # this gets loaded after homing when home_to_max is set
beta_min_endstop 1.26^ #
beta_max_endstop 1.27^ #
beta_homing_direction home_to_min #
beta_min 0 #
beta_max 135 #
gamma_min_endstop nc # Not used, pin is 1.28^
gamma_max_endstop 1.29^ #
gamma_homing_direction home_to_max #
gamma_min -5 #
gamma_max 200 #
# optional order in which axis will home, default is they all home at the same time,
# if this is set it will force each axis to home one at a time in the specified order
homing_order ZXY # x axis followed by y then z last
move_to_origin_after_home true # move XY to 0,0 after homing
# optional enable limit switches, actions will stop if any enabled limit switch is triggered
alpha_limit_enable true # set to true to enable X min and max limit switches
beta_limit_enable true # set to true to enable Y min and max limit switches
gamma_limit_enable true # set to true to enable Z min and max limit switches
alpha_fast_homing_rate_mm_s 5 # feedrates in mm/second
beta_fast_homing_rate_mm_s 5 # "
gamma_fast_homing_rate_mm_s 5 # "
alpha_slow_homing_rate_mm_s 2 # "
beta_slow_homing_rate_mm_s 2 # "
gamma_slow_homing_rate_mm_s 2 # "
alpha_homing_retract_mm 2 # distance in mm
beta_homing_retract_mm 2 # "
gamma_homing_retract_mm 2 # "
#endstop_debounce_count 100 # uncomment if you get noise on your endstops, default is 100
## Z-probe
zprobe.enable true # set to true to enable a zprobe
zprobe.probe_pin 1.28!^ # pin probe is attached to if NC remove the !
zprobe.slow_feedrate 5 # mm/sec probe feed rate
#zprobe.debounce_count 100 # set if noisy
zprobe.fast_feedrate 100 # move feedrate mm/sec
zprobe.probe_height 5 # how much above bed to start probe
#gamma_min_endstop nc # normally 1.28. Change to nc to prevent conflict,
# associated with zprobe the leveling strategy to use
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.enable true # a leveling strategy that probes three points to define a plane and keeps the Z parallel to that plane
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.point1 100.0,0.0 # the first probe point (x,y) optional may be defined with M557
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.point2 200.0,200.0 # the second probe point (x,y)
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.point3 0.0,200.0 # the third probe point (x,y)
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.home_first true # home the XY axis before probing
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.tolerance 0.03 # the probe tolerance in mm, anything less that this will be ignored, default is 0.03mm
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.probe_offsets 0,0,0 # the probe offsets from nozzle, must be x,y,z, default is no offset
#leveling-strategy.three-point-leveling.save_plane false # set to true to allow the bed plane to be saved with M500 default is false
## Panel
panel.enable false # set to true to enable the panel code
# Example for reprap discount GLCD
# on glcd EXP1 is to left and EXP2 is to right, pin 1 is bottom left, pin 2 is top left etc.
# +5v is EXP1 pin 10, Gnd is EXP1 pin 9
#panel.lcd reprap_discount_glcd #
#panel.spi_channel 0 # spi channel to use ; GLCD EXP1 Pins 3,5 (MOSI, SCLK)
#panel.spi_cs_pin 0.16 # spi chip select ; GLCD EXP1 Pin 4
#panel.encoder_a_pin 3.25!^ # encoder pin ; GLCD EXP2 Pin 3
#panel.encoder_b_pin 3.26!^ # encoder pin ; GLCD EXP2 Pin 5
#panel.click_button_pin 1.30!^ # click button ; GLCD EXP1 Pin 2
#panel.buzz_pin 1.31 # pin for buzzer ; GLCD EXP1 Pin 1
#panel.back_button_pin 2.11!^ # back button ; GLCD EXP2 Pin 8
# pins used with other panels
#panel.up_button_pin 0.1! # up button if used
#panel.down_button_pin 0.0! # down button if used
#panel.click_button_pin 0.18! # click button if used
panel.menu_offset 0 # some panels will need 1 here
panel.alpha_jog_feedrate 6000 # x jogging feedrate in mm/min
panel.beta_jog_feedrate 6000 # y jogging feedrate in mm/min
panel.gamma_jog_feedrate 200 # z jogging feedrate in mm/min
panel.hotend_temperature 185 # temp to set hotend when preheat is selected
panel.bed_temperature 60 # temp to set bed when preheat is selected
## Custom menus : Example of a custom menu entry, which will show up in the Custom entry.
# NOTE _ gets converted to space in the menu and commands, | is used to separate multiple commands
custom_menu.power_on.enable false #
custom_menu.power_on.name Power_on #
custom_menu.power_on.command M80 #
custom_menu.power_off.enable false #
custom_menu.power_off.name Power_off #
custom_menu.power_off.command M81 #
## Network settings
network.enable true # enable the ethernet network services
network.webserver.enable true # enable the webserver
network.telnet.enable true # enable the telnet server
#network.ip_address auto # use dhcp to get ip address
# uncomment the 3 below to manually setup ip address
network.ip_address 10.42.200.133 # the IP address
network.ip_mask 255.255.0.0 # the ip mask
network.ip_gateway 10.42.1.1 # the gateway address
#network.mac_override xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx # override the mac address, only do this if you have a conflict
grbl_mode true #for bCNC compatibility
Leveling the base
Leveling of our pexiglass plate took 3 hours. We needed to add some aircooling to prevent melting the plastic. That happened during several tries before. The final result worked out quite well.

 Owls watching the slow process. Almost done.
Owls watching the slow process. Almost done.
Some testing and milling with our new spindle
Who
Goal
- CNC machine voor minstens XY as
- minder dan 500 Euro aan onderdelen
- kop: Dremel boor of extrudeer machine monteerbaar
- suitable for PCB-milling
Electronics
From many electronics options we have chosen to make reprap Generation 7 Electronics. It can drive 4 stepper motors (XYZ and one Extruder), is easy to build, uses common pololu stepper drivers and has many options including electronics for contolling heaters, endstops etc.
The finished electronics (parts for 3D printer left out):
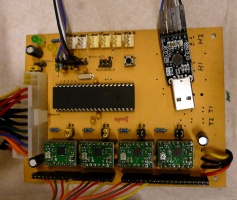
Firmware
Currently we are testing with Teacup Firmware which is supposed to also work for CNC-milling. but the firmware lacks Arc support in Gcode so we might have to switch to Marlin or grbl.
- In the mean time we modified the Teacup firmware so it now supports arcs. The Arc code was taken from Marlin/GBRL and integrated / modified to work with teacup: File:Teacup-ARC-support-v1.0.zip
- Note from the Teacup Maintainer: we had a look at this modified version and found it to be based on 4(!) years old sources. So it misses quite a lot, like a 3-fold performance increase, like Lookahead, like SD card support, like Configtool. To solve this, a branch was created and made up to date. Please give this branch a go (by downloading and using the branch) and tell us how it works. Chances are good to get this into mainline, giving everybody the advantage of this work. --Traumflug (talk) 23:01, 7 April 2016 (CEST)
Cad / Cam and other software
We are testing some software for different purposes:
- Printrun, a utility to control steppers manualy and send gcode to machine
- ReplicatorG, an open source 3D printing program, also with gui to controll the steppers manualy
- GcodeTools plugin for Inkscape so we can use inkscape designs
- pcb-gcode plugin for Eagle for use with pcb milling
Free 3D Modeling Software
- Google SketchUp (requires the freeware plugin to export STL)
- Blender (GPL)
- Art of Illusion (GPL)
- TopMod3D (GPL)
- Wings3D (GPL)
- StructureSynth (GPL)
- OpenSCAD (GPL)
- Heekscad
- FreeCAD
Add ons / Wishlist
List of add ons and options for use with the CNC
- dremel flex shaft mount Peter has designed and printed a similar set of mounts but the flexible dremel shaft was a little bit too flexible. A new design was made and printed by Peter so the dremel is now mounted at the CNC directly.
- Proxxcon IBS/E precision milling tool suitable for SMD pcb milling (hier voor 90 Euro)
- adapter om de IBS/E op de zen toolworks te monteren
(short) PCB milling instructions using eagle with gcode V3.6.4.2 or newer with the TkkrLab CNC (old)
- Make sure the lower left corner of your board is at coaordinates x=0.0, y=0.0
- If you have a double sided board draw a hole of 1.0mm at x0, y0. This helps to allign the board after swapping sides.
- If you want to cut out the board from the pcb after milling and drilling draw some 'wires' around your board in the milling layer (46). The with of the wires should the same with of the milling bit used to cut out the board (2mm is available for this at the moment). The dimention should be your PCB outline + radius of your milling bit.
- Check your board (DRC) with design rules file for eagle: File:Tkkrlab-CNC.zip (needs to be updated for the new settings below)
- Use the following settings File:Tkkrlab cnc20140730.zip for the gcode plugin (Download pcbgcode V3.6.2.4). inside the zip is a readme file that explains how to install and use these settings.
- when all is done split your bottom.drill file in seperate files for drill diameters 0,7mm 0,8mm and 1.0mm. Everything larger then 1.0mm should also be drilled with 1.0mm and can be manually drilled with a larger bit after your board is finished.
- Place your PCB material against the x-axis and set your home (0.0) position on the lower left on the pcb. If you cut out your board afterwards leave enough room for the mill bit you use for that
- Put a piece of scratch (but evenly thick) wood under your board so you not cut or drill into the bottom plate.
- for single side boards: bottom milling and after that use your splitted drill files to drill the holes using the correct drill bit for each file.
- for double sided boards: First drill a 1mm hole at 0.0. Then start top milling, wait until ready and then turn around your board and place it again agains the x-axis. Allign your board using your drilled hole and home the CNC to that. Start milling the bottom layer and finaly use your splitted drill files to drill the holes using the correct drill bit for each file.
- end cut out milling: Make sure the cnc is still aware of the correct coordinates (go to 0.0 and check if it at correct). Place the miling bit, home the Z axis and use the bott.mill file to cut out our board. (press the board down a bit when its almost finished and becomes loose).
PCB milling instructions using eagle with the TkkrLab CNC (new)
| download pcb-gcode-2.6.2.4 and unzip it in a new folder called "pcbgcode" in your Eagle directory. | 400px |
| download File:Tkkrlab cnc gcode settings.zip and unzip it in ../eagle/pcbgcode/settings/ | 400px |
| download File:Tkkrlab-CNC.zip and unzip it in ../ealge/dru/ | 400px |
| start eagle and draw a pcb or something. | 400px |
| If you want to cut out the board from the pcb after milling and drilling draw some 'wires' around your board in the milling layer (46). The with of the wires should the same with of the milling bit used to cut out the board (2mm is available for this at the moment). The dimention should be your PCB outline + radius of your milling bit. | 400px |
| If you are using a groundplane, set the isolation to minimal 0.6mm (right click polygon, properties) if it´s possible in your project. | 400px |
| check your pcb with the dru file you have placed in the ../eagle/dru/ directory. | 400px |
| press the ULP button and run ../eagle/pcbgcode/pcb-gcode-setup.ulp | 400px |
| Go to the plugins tab and select the settings file ../settings/saved/tkkrlab_cnc.def and click Load. | 400px |
| goto the GCode Style tab, select generic. | 400px |
| Go to the Machine tab and select the Default drill Rack file tkkrlab_cnc.drl | 400px |
| Maybe you want to change your drill depth at the Machine tab. And change the milling option (and depth) at the general tab. And press "accept and make my board". | 400px |
| You will get a picture of the gcode. Brown means that the CNC is passing that trace one time. Red means it´s passing it 2 times. (2 times is better) | 400px |
| If it´s fine, press Q. You will get new *.ngc files in your project directory. Move it to a USB stick. | 400px |
| Add "G00 X0 Y0" in every ngc file you have created after "G00 Z10.0000" (that´s before "M05") (it´s on the end of the file) | 
|
| Open *.bot.drill.ngc on your USB stick and check the tool sizes in the comments of the file. | 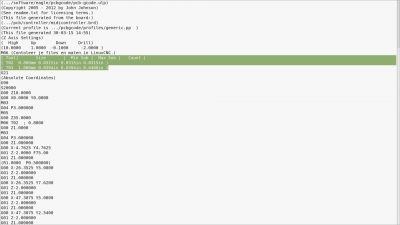
|
| If you want to drill al the holes with the same size, delete this part for every tool. (tip: ctl-f for the tools you have, for example: T02) | 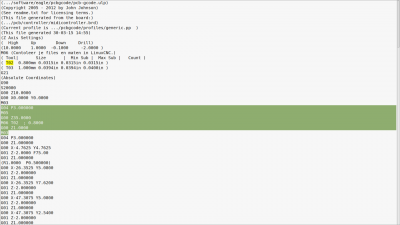
|
| If you want to drill with different sizes, split the file in different files, for each drill one file. And delete "M06 T0.. ; ....." | 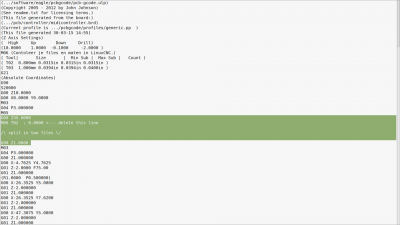
|
| Go to the cnc pc and put your USB stick into the pc. | 400px |
| coming soon |